A) average saving rate
B) output-to-capital ratio
C) marginal tax rate on investment
D) depreciation rate
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4 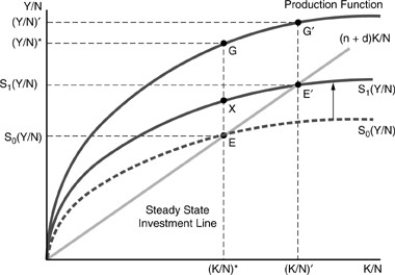 -Which of the following is not a reason for differences in per capita income in neoclassical growth theory?
-Which of the following is not a reason for differences in per capita income in neoclassical growth theory?
A) All countries have the same production function.
B) Countries have different savings rates.
C) The slope of the steady-state investment line is different for different countries.
D) all of the above.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-2 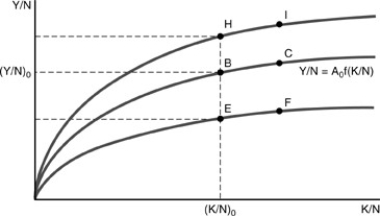 -In the context of growth, the goal of stabilization policy once per capita output is equal to potential per capita output is to
-In the context of growth, the goal of stabilization policy once per capita output is equal to potential per capita output is to
A) insure that the percentage change in per capita output and potential per capita output over time are equal.
B) raise the growth rate of potential per capita output above that of per capita output.
C) raise the growth rate of per capita output above that of potential per capita output.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an equal percentage increase in the factors of production raises real GDP by the same percentage, the production function has the characteristic known as
A) constant returns to scale.
B) constant marginal productivity.
C) diminishing marginal productivity.
D) increasing returns to scale.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A convenient rule of thumb called the "rule of 72" states that a quantity growing at x percent per year doubles in size approximately every (72/x) years. -Refer to the information above. An economy's real GDP per person doubles every 18 years when it maintains a growth rate of ________ per year.
A) 5.6 percent
B) 4.0 percent
C) 0.25 percent
D) 0.9 percent
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic growth theory studies how real GDP changes ________, in other words the growth of ________ real GDP.
A) on average over long periods, natural
B) on average over long periods, actual
C) from one year to the next, natural
D) from one year to the next, actual
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Chapter 10, depreciation is assumed to be
A) a fixed proportion of real GDP.
B) a fixed proportion of the capital stock.
C) a fixed absolute amount.
D) zero.
E) a fixed proportion of the capital-labor ratio.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are not examples of "convergence"?
A) Japan and Europe
B) Individual states within the United States
C) regions within western Europe
D) major nations in Latin America and Western Europe
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4  -Which of the following is not a real world factual conflict with the neoclassical growth model?
-Which of the following is not a real world factual conflict with the neoclassical growth model?
A) Income per capita varies greatly across countries.
B) Poor countries do not have a higher rate of return on capital.
C) Immigrant labor from poor countries experiences very small increases in income when it moves to rich countries.
D) poor countries' income levels have not converged to the income levels of rich countries.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The application of Solow's growth theory to the explanation of the slowdown in productivity growth in the United States suggests that the slowdown is primarily caused by
A) reduced growth in the capital stock per hour of work.
B) reduced growth in the technical change or total factor productivity.
C) slow residual growth of the capital stock.
D) ignorance since people save and invest less.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the context of the neoclassical growth model, which of the following does not explain the growth rates of countries which are initially poor?
A) nations which are below their steady-state growth paths will grow more slowly until they reach the steady state
B) the rate of return is higher in poor countries
C) capital flows from rich countries to poor countries
D) the passage of time allows poor countries to adopt the productive techniques of rich countries.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4  -Initially, the economy is at point G in the figure above An increase in per capita savings from s(0) to s(1) will in the short run result in ________ and in the long run result in ________.
-Initially, the economy is at point G in the figure above An increase in per capita savings from s(0) to s(1) will in the short run result in ________ and in the long run result in ________.
A) excess per capita saving; more rapid growth in per capita output
B) excess per capita saving; less rapid growth in per capita output
C) more rapid growth in per capita output; more rapid growth in per capita output
D) more rapid growth in per capita output; no change in the long run rate of growth in per capita output
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If K = 3000, n = 0.015, and d = 0.082, then investment of ________ will hold (Y/N) constant.
A) 291
B) 201
C) 164
D) 549
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From an initial steady state, suppose a government policy increases the national saving rate, causing the capital stock to start growing faster than the population. With (K/N) now rising, the Solow growth model goes on to say that (Y/N)
A) will rise only so far, to where the increased requirement for new capital matches the increased saving.
B) will rise only temporarily, so long as the population growth rate remains constant.
C) will rise and keep on rising, so long as the national saving rate exceeds the population growth rate.
D) never does rise, since the government's policy does not affect either the population growth rate or the depreciation rate.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The per person production function representing both physical capital per person (K/N) and human capital per person (H/N) is
A) Y/N = (K/N) b(H/N) c
B) Y/N = (K/N) b + (H/N) c
C) Y/N = (K/N) b - (H/N) c
D) Y/N = (K/N) b/(H/N) c
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4  -Given that all countries have the same Cobb-Douglas production function, i.e. Y/N = (K/N) b, a ten-fold difference in per capita income requires a difference in capital per capita by a factor of
-Given that all countries have the same Cobb-Douglas production function, i.e. Y/N = (K/N) b, a ten-fold difference in per capita income requires a difference in capital per capita by a factor of
A) 10.
B) 10b.
C) 101/b.
D) b.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Private investment is equal to the net addition to the capital stock ________ the depreciation of that capital stock.
A) plus
B) minus
C) times
D) divided by
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-5 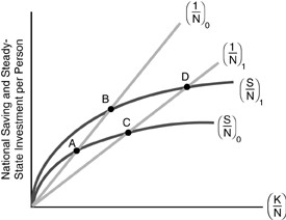 -In the figure above, suppose that the population growth rate declines. This causes a movement of the steady-state point such as from points
-In the figure above, suppose that the population growth rate declines. This causes a movement of the steady-state point such as from points
A) A to B.
B) D to B.
C) D to C.
D) A to C.
E) A to D.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When we study economic growth, we are most concerned about changes in
A) the output ratio.
B) the level of natural real output.
C) the absolute difference between natural and actual real output.
D) None of these.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rise in the multifactor productivity index means that at each (K/N) we have (Y/N) ________, which shifts the (S/N) curve ________, resulting in a movement of the steady-state intersection to the ________.
A) rising, downward, left
B) rising, upward, right
C) rising, downward, right
D) falling, upward, left
E) falling, downward, left
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 113
Related Exams