A) national income.
B) aggregate supply.
C) aggregate demand.
D) disposable income.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classical macroeconomic model argues that the economy has built-in forces that automatically eliminate unemployment and quickly move the economy to its full employment level of real GDP.Which assumption is critical to this argument?
A) Rigid wages and prices
B) Flexible wages and prices
C) Natural rate of unemployment
D) Profit motive
E) None of the choices are correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The line segment QR describes the region where
A) increases in output do not cause higher prices because of a large portion of unemployed resources.
B) prices and output increase together.
C) increases in prices do not generate any increase in output.
D) increases in prices cause decreases in output.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the aggregate supply curve is horizontal,
A) there are unemployed resources.
B) the economy is inside the production possibilities frontier.
C) it is possible to increase output,without driving up prices,by putting unemployed resources to work.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynesian theory
A) changes in the equilibrium interest rate will not always equate saving and investment.
B) prices and wages are flexible downward.
C) Say's law is valid.
D) savers and investors have identical motives.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Say's law
A) was a basic pillar of classical economics.
B) was a basic pillar of Keynesian economics.
C) was formulated during the Great Depression.
D) proves that we can never have full employment.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The curve showing the amount of real output,or real GDP,that will be made available by sellers at various price levels is called the
A) aggregate demand curve.
B) real gross domestic investment curve.
C) aggregate supply curve.
D) Keynesian cross.
E) aggregate individual demand curvE.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classicals believed that when savings exceeds investment,
A) demand is reduced and the economy will go into a recession.
B) the interest rate will decline and equate savings and investment.
C) an increase in supply will encourage higher investment spending.
D) if savings is greater than investment unemployment would reduce savings.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes's analysis of the Great Depression led to which of the following recommendations regarding government policy?
A) An annually balanced budget.
B) A decrease in government spending.
C) An increase in government spending.
D) An increase in taxes.
E) Government should pursue a laissez-faire attitudE.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following assumptions is crucial to the classical macroeconomic model's assertion that the economy has built-in forces that automatically eliminate unemployment and quickly move the economy to its potential level of real GDP?
A) Profit motive
B) Rigid wages and prices
C) Flexible wages and prices
D) Natural rate of unemployment
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
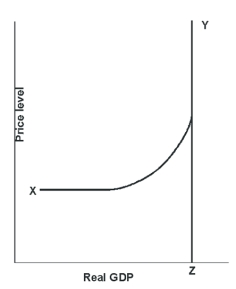 -Curve YZ represents ____________.
-Curve YZ represents ____________.
A) short-run aggregate demand
B) long-run aggregate demand
C) short-run aggregate supply
D) long-run aggregate supply
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The classical theory predicts that decreases in the supply of savings will _______ interest rates and _______ investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In analyzing recessions,Keynes' view was that
A) the economy may eventually recover by itself,but it takes too long.
B) the government could stimulate aggregate purchases by reducing the budget deficit.
C) the economy will never recover because wages and prices will never adjust downward.
D) any cyclical unemployment will be short-lived,and thus there is no need for increased government spending.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
John Maynard Keynes would argue that massive government spending ___________ will pull us out of a depression.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the nation is in a recession.As a result,the current macroeconomic equilibrium occurs along the flat portion of the aggregate supply curve.A moderate increase in aggregate demand is likely to
A) increase the equilibrium price level with little effect on equilibrium real GDP.
B) increase equilibrium real GDP with little effect on the price level.
C) cause the price level to fall.
D) decrease employment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following does NOT explain why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping?
A) The loanable funds effect
B) The real balances effect
C) The foreign purchases effect
D) The interest rate effect
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the average price level in the United States,relative to the average price levels in other countries,rises,this tends to
A) raise imports and exports.
B) lower imports and exports.
C) raise imports and lower exports.
D) lower imports and raise exports.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The notion that "no man produces but with a view to consume or sell,"
A) sums up Say's Law.
B) can be restated as "supply creates it own demand."
C) was said by David Ricardo,elaborating on Say's Law.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classical theory of the loanable funds market concluded that
A) Saving and investment would not be equal because of changes in the volume of bank credit.
B) An increase in the desire to save would increase the interest rate and lower the volume of investment.
C) The interest rate would equate saving and investment and thereby undermine Say's law.
D) The interest rate would equate saving and investment and thereby cause Say's law to be valiD.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Classical employment theory holds that
A) wages are flexible upward and downward in the long run.
B) an excess of saving over investment (a surplus in the loanable funds market) at any given interest rate will cause the interest rate to fall.
C) unemployment will cause wages and prices to decline.
D) All of the choices are true of classical employment theory.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 241
Related Exams