A) an inflationary gap equal to $100 billion.
B) an inflationary gap equal to $50 billion.
C) a recessionary gap equal to $50 billion.
D) a recessionary gap equal to $100 billion.
E) neither an inflationary nor a recessionary gap because the economy is at full employment.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We observe an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP. Which of the following is a possible explanation?
A) a decrease in the quantity of money
B) a decrease in expected future income
C) an increase in factor prices
D) an increase in the quantity of capital
E) an increase in expected future profits
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following variables can change without creating a shift of the aggregate demand curve?
A) the interest rate
B) price level
C) the tax rate
D) expectations about inflation
E) monetary policy
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the actual unemployment rate is equal to the natural unemployment rate, then the
A) inflation rate must be zero.
B) long-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping.
C) short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) economy is operating at potential GDP.
E) the money wage rate will rise.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
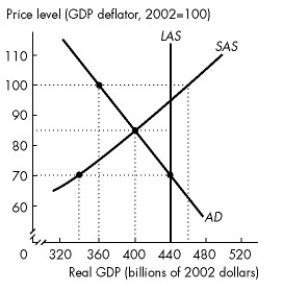 Figure 26.3.1
-Refer to Figure 26.3.1. Consider statements (1) and (2) and select the correct answer. (1) The economy of Econoworld is experiencing a below full-employment equilibrium.
(2) The actual unemployment rate equals the natural unemployment rate.
Figure 26.3.1
-Refer to Figure 26.3.1. Consider statements (1) and (2) and select the correct answer. (1) The economy of Econoworld is experiencing a below full-employment equilibrium.
(2) The actual unemployment rate equals the natural unemployment rate.
A) (1) is true; (2) is false.
B) (2) is true; (1) is false.
C) (1) and (2) are false.
D) (1) and (2) are true.
E) (1) is true; (2) is true if the natural unemployment rate is too high.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there is an increase in the quantity of capital. As a result, the SAS
A) and the LAS curves both shift leftward.
B) and the LAS curves both shift rightward.
C) curve does not shift but the LAS curve shifts rightward.
D) curve does not shift but the LAS curve shifts leftward.
E) curve shifts rightward, but the LAS curve does not shift.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following events: Event 1: Growth in the world economy slows. Event 2: The world price of oil rises. Event 3: Canadian labour productivity declines. Choose the statement that is correct.
A) A classical macroeconomist and a monetarist recommend that taxes be kept low to avoid disincentive effects for all of the events and a Keynesian recommends active fiscal policy and monetary policy to offset all events.
B) All macroeconomists believe that the economy requires active fiscal policy and monetary policy to keep the economy out of recession.
C) A classical macroeconomist and a monetarist recommend an increase in the quantity of money for all events.
D) A Keynesian recommends no action for all of the events.
E) A Keynesian recommends active fiscal policy but not monetary policy for events 1 and 2 and monetary policy but not fiscal policy for event 3.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following question.
Table 26.3.2
 -Refer to Table 26.3.2. The International Monetary Fund's World Economic Outlook database provides the data given in the table for India in 2004, 2005 and 2006. The numbers in the table are consistent with
-Refer to Table 26.3.2. The International Monetary Fund's World Economic Outlook database provides the data given in the table for India in 2004, 2005 and 2006. The numbers in the table are consistent with
A) increases in long-run and short-run aggregate supply and even greater increases in aggregate demand.
B) increases in short-run aggregate supply and increases in aggregate demand, but the increases in aggregate demand are smaller than the increases in short-run aggregate supply.
C) increases in long-run and short-run aggregate supply and even larger decreases in aggregate demand.
D) decreases in long-run and short-run aggregate supply and even greater decreases in aggregate demand.
E) increases in short-run aggregate supply and no change in aggregate demand.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Disposable income is aggregate income
A) minus taxes and benefits.
B) minus taxes plus transfer payments.
C) minus fixed expenses such as rent and utilities.
D) plus transfer payments.
E) minus taxes.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
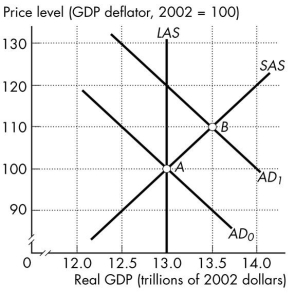 Figure 26.3.5
-Refer to Figure 26.3.5. At point B the economy has
Figure 26.3.5
-Refer to Figure 26.3.5. At point B the economy has
A) an inflationary gap with real GDP in excess of potential GDP.
B) an inflationary gap with real GDP less than potential GDP.
C) a recessionary gap with real GDP in excess of potential GDP.
D) a recessionary gap with real GDP less than potential GDP.
E) neither an inflationary gap nor a recessionary gap.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity of real GDP demanded is the sum of real consumption expenditure (C) , investment (I) ,
A) government expenditure (G) , exports (X) , and imports (M) .
B) government expenditure (G) , and exports (X) minus imports (M) .
C) exports (X) , and imports (M) .
D) and exports (X) minus imports (M) .
E) and government expenditure (G) .
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
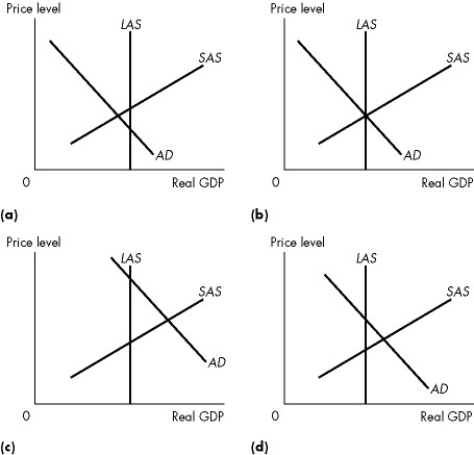 Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3(a) . You might expect the government to
Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3(a) . You might expect the government to
A) do nothing except maintain the current equilibrium.
B) cut government expenditure.
C) increase government expenditure.
D) pursue trade policies that reduce exports.
E) raise taxes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Everything else remaining the same, an increase in the quantity of money
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B) shifts the aggregate demand curve leftward.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve leftward.
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve rightward.
E) creates a movement down along the aggregate demand curve.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following will raise the price level except
A) aggregate demand increases and short-run aggregate supply decreases.
B) aggregate demand increases.
C) short-run aggregate supply decreases.
D) an increase in the quantity of capital.
E) an increase in the quantity of money.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3. In which of the graphs would we predict that eventually the price level will rise and real GDP will fall, all else remaining the same?
Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3. In which of the graphs would we predict that eventually the price level will rise and real GDP will fall, all else remaining the same?
A) (a) only
B) (b) only
C) (c) only
D) (d) only
E) both (c) and (d)
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3. Which one of the graphs illustrates a below full-employment equilibrium?
Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3. Which one of the graphs illustrates a below full-employment equilibrium?
A) (a) only
B) (b) only
C) (c) only
D) (d) only
E) both (c) and (d)
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 26.3.1
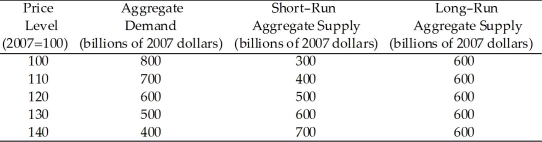 -Refer to Table 26.3.1. Consider the economy represented in the table. In short-run macroeconomic equilibrium, the price level is ________ and the level of real GDP is ________ billion.
-Refer to Table 26.3.1. Consider the economy represented in the table. In short-run macroeconomic equilibrium, the price level is ________ and the level of real GDP is ________ billion.
A) 120; $600
B) 120; $500
C) 125; $550
D) 130; $600
E) 130; $500
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the money wage rate falls, then
A) the AD curve shifts rightward.
B) firms hire less labour.
C) the LAS curve shifts rightward.
D) the SAS curve shifts rightward.
E) the LAS curve and the SAS curve shift rightward.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3. Which one of the graphs illustrates a full-employment equilibrium?
Figure 26.3.3
-Refer to Figure 26.3.3. Which one of the graphs illustrates a full-employment equilibrium?
A) (a) only
B) (b) only
C) (c) only
D) (d) only
E) (c) and (d)
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
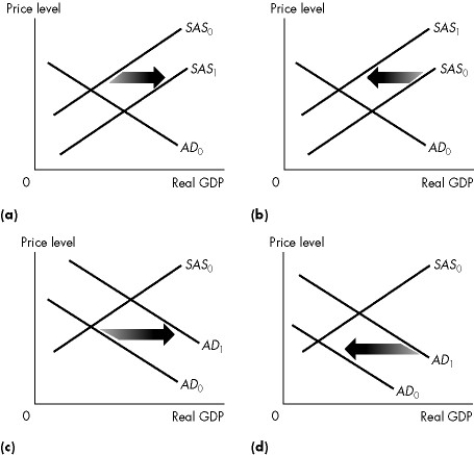 Figure 26.2.1
-Refer to Figure 26.2.1. Which graph illustrates what happens when government expenditure decreases?
Figure 26.2.1
-Refer to Figure 26.2.1. Which graph illustrates what happens when government expenditure decreases?
A) (a) only
B) (b) only
C) (c) only
D) (d) only
E) Both (a) and (d)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 136
Related Exams