A) is absolutely necessary for prudent management of the economy.
B) is the same as an annually balanced budget.
C) is a worthy idea but requires accurate forecasting and definition of the business cycle.
D) would be pro-cyclical.
E) would stabilize the economy and produce an annual budget balance of zero.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose legislation in Canada required annually balanced government budgets.This legislation would
A) require the Bank of Canada to expand and contract the money supply according to an annual timetable.
B) force a balanced budget that could turn a minor downturn in the economy into a serious and prolonged recession.
C) force increased levels of government spending automatically increasing the size of the government debt.
D) allow deficits but prevent the government from running surpluses.
E) require the Bank of Canada to lower interest rates during periods of inflation.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The 2008-2009 global recession had an effect on Canadian federal and provincial budgets.In general,government debt-to-GDP ratios rose in Canada because of
A) contractionary monetary policy and expansionary fiscal policy.
B) an increased burden of debt-service payments due to the necessary reduction in the target overnight interest rate by the central bank.
C) the decline in net tax revenues due to the recession,as well an expansionary fiscal policy.
D) the necessity to balance the primary budget at the same time that the interest rate on government debt was rising.
E) the necessity to balance the cyclically adjusted budget at the same time that the interest rate on government debt was rising.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a government with an outstanding stock of public debt.If,in any given year,the government has a primary budget surplus and the real interest rate on government bonds is less than the growth rate of real GDP,then
A) debt-service payments will be eliminated.
B) the debt-to-GDP ratio is certainly negative.
C) the debt-to-GDP ratio will certainly rise.
D) the debt-to-GDP ratio will certainly fall.
E) real GDP will certainly rise.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a closed-economy AD/AS model.If an increase in the government's budget deficit drives up market interest rates,
A) credit will become less expensive.
B) nothing - government borrowing cannot push up interest rates.
C) private expenditure will likely increase.
D) some private investment expenditure will probably be crowded out.
E) the money supply will increase.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the stock of government debt in Canada at the end of fiscal Year 1 is $475 billion.If the stock of debt falls to $461 billion by the end of fiscal Year 2,then we know that during Year 2
A) the government had a primary budget surplus of $14 billion.
B) the government had a primary budget deficit of $14 billion.
C) tax revenues increased by $14 billion.
D) the government had an annual budget surplus of $14 billion.
E) debt-service payments fell by $14 billion.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following variables: G = government purchases I = interest rate on government debt D = stock of government debt T = net tax revenue The government's budget deficit can be expressed as
A) ΔD = (G + iD) - T.
B) ΔD = (G - iD) + T.
C) deficit = D - (G + iD) + T.
D) deficit = D - T + (G + iD) .
E) T = ΔD - (G + iD) .
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the stock of government debt in Canada at the end of fiscal Year 1 is $475 billion.If the stock of debt falls to $461 billion by the end of fiscal Year 2,and debt-service payments during Year 2 were $38 billion,then we know that the government had
A) a primary budget surplus of $52 billion.
B) a primary budget surplus of $14 billion.
C) a primary budget surplus of $24 billion.
D) an annual budget surplus of $38 billion.
E) an annual budget deficit of $14 billion.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy goes into a recession,the structural budget deficit is most likely to
A) increase,because government expenditures and tax revenues will both rise.
B) increase,because government expenditures will rise and tax revenues will decline.
C) remain unchanged,although there will be a primary budget surplus.
D) remain unchanged,unless government actively changes its fiscal policy.
E) decrease,because government expenditures will decrease and tax revenues will rise.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run,the government budget will add to sustained inflation if
A) they require decreases in the money supply.
B) continual deficits are financed by the continual creation of new money.
C) deficits are always accompanied by decreases in the money supply.
D) government borrowing lowers interest rates.
E) the government finances the deficit by borrowing from the private sector.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The extent to which tax revenues are able to finance the discretionary part of total government expenditure is best measured by the
A) cyclically adjusted deficit/surplus.
B) government's current fiscal policy.
C) debt-to-GDP ratio.
D) government's primary budget deficit or surplus.
E) tax-to-GDP ratio.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows government purchases (G) ,net tax revenues (T) ,and debt-service payments (iD) over a 4-year period for a hypothetical economy.All figures are in billions of dollars.Assume the stock of debt at the end of 2015 is $500 billion. 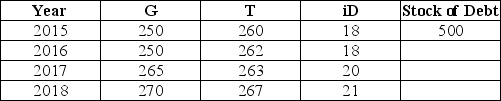 TABLE 31-1 Refer to Table 31-1.What is the stock of debt at the end of 2016?
TABLE 31-1 Refer to Table 31-1.What is the stock of debt at the end of 2016?
A) $488 billion
B) $494 billion
C) $500 billion
D) $506 billion
E) $512 billion
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows the budget deficit function for a government in a hypothetical economy. 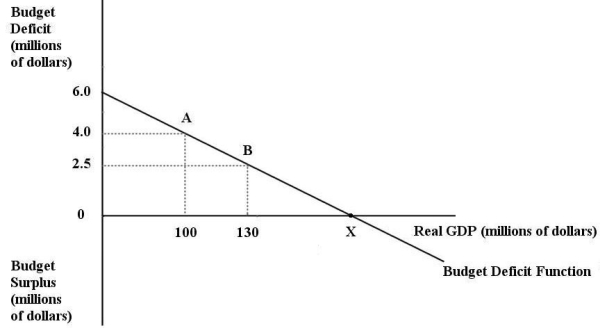 FIGURE 31-1 Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A on the graph.Which of the following is consistent with a move from point A to point B?
FIGURE 31-1 Refer to Figure 31-1.Initially,suppose real GDP is $100 million and the budget deficit is $4 million,as shown by point A on the graph.Which of the following is consistent with a move from point A to point B?
A) implementation of an expansionary fiscal policy
B) implementation of a contractionary fiscal policy
C) implementation of a contractionary monetary policy
D) the economy entering into a recession
E) the economy entering into a boom
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following data about government debt and deficit in a given year: - real interest rate on government bonds = 3% - growth rate of real GDP = 3% - current debt-to-GDP ratio = 25% - primary budget surplus as a percentage of GDP = 2% Over this one-year period,the debt-to-GDP ratio will have
A) remained unchanged.
B) risen by 0.2 percentage points.
C) fallen by 0.2 percentage points.
D) risen by 2 percentage points.
E) fallen by 2 percentage points.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the government's budget deficit function,graphed with dollars on the vertical axis and real GDP on the horizontal axis.This function is downward sloping because as real GDP
A) falls,the budget deficit function shifts down.
B) falls,tax revenues rise,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
C) rises,tax revenues rise,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
D) rises,tax revenues fall,decreasing the deficit or increasing the surplus.
E) rises,it leads to increasing debt-service payments.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Do we get a useful and meaningful statistic by dividing the national debt by the GDP?
A) No - we are essentially "dividing apples by oranges," which is unhelpful.
B) No - the GDP is not a meaningful measure of the well-being of the economy.
C) Yes - we can then see how much of the national debt is owed by each individual citizen.
D) Yes - we can see the burden of the debt in relation to the size of the economy.
E) No - dividing a stock by a flow can never be sensible.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Canadian tax and transfer system acts as an automatic stabilizer because
A) net tax revenues decrease during economic booms and decrease during economic recessions.
B) net tax revenues increase during economic booms and decrease during economic recessions.
C) tax rates will automatically decrease to stimulate the economy during economic booms.
D) tax rates will automatically increase if the government is running deficits.
E) tax rates will automatically increase to stimulate the economy during economic recessions.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows two budget deficit functions for a hypothetical economy. 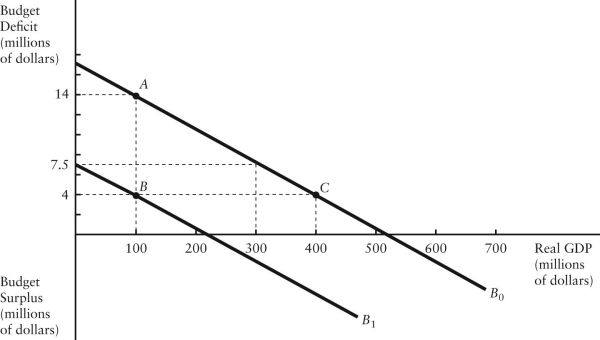 FIGURE 31-2 Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function
FIGURE 31-2 Refer to Figure 31-2.Initially,suppose the economy is at point A on budget deficit function  .Real GDP (Y) is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*) were $300 million,the structural budget deficit would be
.Real GDP (Y) is $100 million.If the level of potential output (Y*) were $300 million,the structural budget deficit would be
A) $2 million.
B) $14 million.
C) measured by the vertical distance between the horizontal axis and ![]() (at real GDP = 300) .
(at real GDP = 300) .
D) measured by the vertical distance between point A and the budget deficit that would exist at real GDP = 300 million.
E) Insufficient information to know.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the government's budget constraint.The accumulated stock of government debt will begin to fall
A) if the government's debt-service payments are zero.
B) if the government does not borrow money.
C) if the growth rate of real GDP is higher than the real interest rate.
D) when the government's annual budget is in deficit.
E) when the government's annual budget is in surplus.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The data below provides the Actual and Structural Budget Deficits,as a percentage of real GDP,for Canada between 1999 and 2010.Note that a negative value in the table indicates a budget surplus. 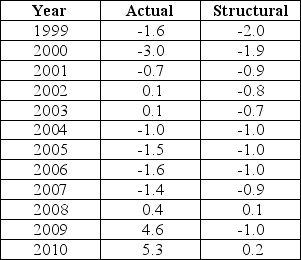 TABLE 31-2 Refer to Table 31-2.Consider the years 2008-2010.The fact that the actual budget deficit in each year was greater than the structural budget deficit reflects the fact that
TABLE 31-2 Refer to Table 31-2.Consider the years 2008-2010.The fact that the actual budget deficit in each year was greater than the structural budget deficit reflects the fact that
A) output was equal to potential.
B) fiscal policy was contractionary over that time.
C) fiscal policy was expansionary over that time.
D) actual GDP was less than potential in each of those years.
E) actual GDP was greater than potential in each of those years.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 125
Related Exams